Last updated on October 1st, 2021 at 01:36 am
How SSL certificates work diagram illustrates how the client applications and server communicate securely in an insecure network such as the internet. In this article, I explore this topic to help understand how SSL adds an extra layer of security.
Before diving into the topic, here are some cryptographic algorithms used in the SSL protocol that you need to understand.
Symmetric vs Asymmetric encryption
Encryption is a process of converting plain text into an intelligible format (Ciphertext). Symmetric encryption( also known as private key encryption) uses a single key for both encryption and decryption of the message.
On the other hand, Asymmetric encryption( also known as public-key encryption) uses different keys for encryption and decryption. Public key encryption uses the public key for encryption and the private (secret key) for decryption. The public key can be shared while the private key is never transmitted or shared on a network.
What is an SSL certificate?
SLS certificate is a data file that binds a cryptographic key to organization details. When the certificate is installed in the web server, it activates the HTTPS protocol and ensures a secure connection between the client’s agent such as browsers and the server.
How SSL certificates work diagram
The server and the client( browser) exchanges information through a series of the client hello and server hello messages referred to as SSL handshake. The server and the client exchange cryptographic information such as the Session key, certificate, and public key of the server.
The SSL handshake process occurs within a short time to notice. If you have browsed on an HTTPS enabled website then you have experienced the SSL handshake.
There are two types of SSL handshake:
- One-way handshake
Here, only the client verifies the server. Such as browser-to-server communication
- 2- way handshake
In this type, both the client and the server verify each other. Such as in server-to-server communication
When you connect using the HTTP protocol, all information sent on the network is transmitted in plain text, and it is susceptible to attacks such as eavesdropping.
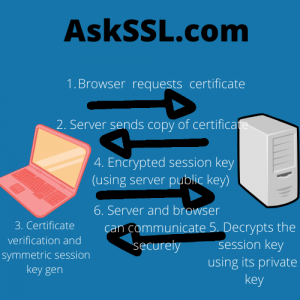
The image illustrates how the browser and the server establish secure communication.
Step 1: Browser request the certificate
The browser requests the certificate from the server. This is the certificate that was issued from the certificate authority, CA.
-
Server responds with a copy of the certificate
Upon receiving the request from the client, the server sends back a copy of its certificate. The certificate contains the public of the server and the common name of the website among other information.
-
Verification
The browser maintains a list of pre-installed CA in its trusted root CA store. The browser checks the root against the list of trusted CA and verifies if the certificate is unrevoked and unexpired. The browser retrieves the public key of the server from the certificate.
Also, the browser checks the common name is valid for the website connection. The browser generates a symmetric key for encryption.
NB
Though public key encryption is more secure, it requires a lot of processing power hence its only use for secret key exchange.
-
The browser sends the encrypted session key back to the server.
Here, the browser encrypts the generated symmetric session key and sends it back to the server.
-
Server decrypts the session key
Upon receiving the session key, the server decrypts the cipher with its private key (The private key is created when the certificate is issued and it’s never shared).
-
Server and the browser can now communicate securely.
Since both, the browse and the server have a copy of the symmetric session key, the sender encrypts the data using the session key and the receiver can decrypt.
Conclusion
As forementioned, how SSL certificates work diagram is aimed to visualize how clients and servers transmit data over an insecure internet.
SSL protocol is secure and ensures parties can participate and transmit sensitive information in a trusted and more secure way.
